Over the past five years, nuclear energy has consistently supplied around 20% of Spain’s electricity.
Over the past five years, nuclear energy has consistently supplied around 20% of Spain’s electricity. Despite this stability, the sector is the subject of ongoing debate regarding its future role in maintaining grid reliability, particularly following the widespread blackout in April 2025, which highlighted the challenges of integrating high shares of variable renewable generation.
The Consejo de Seguridad Nuclear (CSN), Spain’s independent nuclear safety regulator, oversees plant safety, radiation protection, and operational compliance. Broader energy policy is coordinated by the Secretary of State for Energy, under the Ministry for the Ecological Transition, in collaboration with the National Markets Commission.
Spain imports all its uranium and employs an open fuel cycle without reprocessing spent fuel. The General Radioactive Waste Plan, updated in 2023, outlines strategies for decommissioning and disposal. Low- and intermediate-level waste is stored at the El Cabril facility near Córdoba, while spent fuel is held in temporary on-site storage, such as at the Trillo plant. Plans for a centralized temporary storage facility in Villar de Cañas aim for commissioning around 2028.
In 2024, Spain’s seven operational reactors produced approximately 52.4 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity, down from 54.4 TWh in 2023, showing a modest decline. Nuclear power accounted for 19.98% of net electricity production in 2024, ranking as the country’s second-largest source after renewables. According to data from the global energy think tank Ember, 77% of Spain’s electricity generation in 2024 came from low-carbon sources, with wind (22%), solar (21%), and nuclear (20%) contributing nearly equal shares. Nuclear capacity stands at 7,117 megawatts (MW), representing 5.52% of Spain’s total installed net generation capacity of approximately 129,000 MW.
The current reactor fleet, commissioned in the 1980s, consists of pressurized water reactors. No new units are under construction. Even with cost reductions and accelerated schedules—estimated at around €4,000 per kilowatt—analyses suggest the economically optimal nuclear share in Europe would be about 10%.
Operational costs for nuclear power in Spain exceed €50 per megawatt-hour, with roughly 40% attributed to taxes and fees. These include contributions to ENRESA, the state-owned entity responsible for radioactive waste management and plant decommissioning. In 2024, ENRESA’s waste-management levy increased by 30%, adding further cost pressures.
Plant life extensions beyond the original 40-year design lifespan require CSN safety approval. According to Spain’s nuclear phase-out plan, decommissioning is scheduled to begin in 2027 as reactors reach their operational limits. However, following the April 2025 blackout, calls have intensified within the industry to extend the operating lives of existing plants. While nuclear’s share of Spain’s generation mix has declined relative to renewables, it continues to provide a dependable source of baseload power. Recent disruptions to grid stability have prompted renewed discussion about whether nuclear energy should retain a stronger role as a stabilizing force in Spain’s increasingly renewable-dominated system.
This Post was submitted by Climate Scorecard Spain Country Manager, Juanjo Santos.
NUCLEAR POWER PLANTS AND REACTORS IN SPAIN
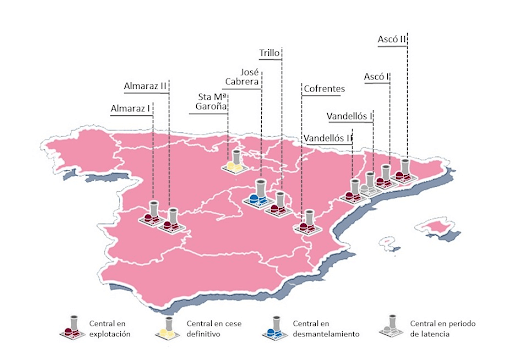
In Spain, there are five nuclear power plants in operation, located in 5 locations (see attached table), two of which have two reactors each (Almaraz and Ascó), for a total of seven light water reactors.
Almaraz Nuclear Power Plant I – Operational plant located in Almaraz, province of Cáceres.
Almaraz Nuclear Power Plant II – Operational plant located in Almaraz, province of Cáceres.
Ascó Nuclear Power Plant I – Operational plant located in Ascó, province of Tarragona.
Ascó Nuclear Power Plant II – Operational plant located in Ascó, province of Tarragona.
Cofrentes Nuclear Power Plant – Operational plant located in Cofrentes, province of Valencia.
José Cabrera Nuclear Power Plant – Decommissioning plant located in Almonacid de Zorita, province of Guadalajara.
Santa María de Garoña Nuclear Power Plant – Decommissioning plant located in Valle de Tobalina, province of Burgos.
Trillo Nuclear Power Plant – Operational plant located in Trillo, province of Guadalajara.
Vandellós Nuclear Power Plant I – Decommissioning plant located in Vandellòs and L’Hospitalet de l’Infant, province of Tarragona.
Vandellós Nuclear Power Plant II – Operational plant located in Vandellòs and L’Hospitalet de l’Infant, province of Tarragona.

